Programming #101: The Line Follower Principle
A basic line follower algorithm is used on an autonomous robot that can follow either a black line on white area or white line on black area. It is expected to be able to detect a line and follow it. There are two popular kinds of line follower that one can develop for their EV3 robots. These are the Switch Line Follower and Proportional Line Follower.
Switch Line Follower
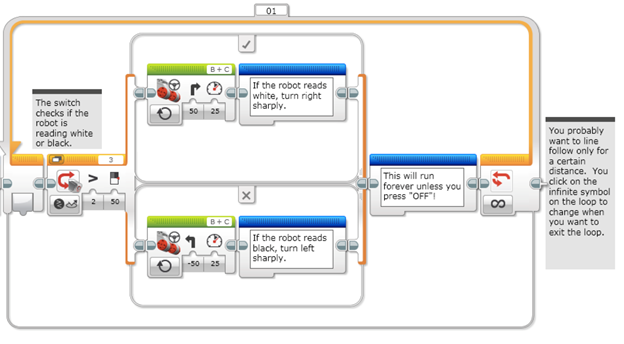
The Switch Line Folllower requires the use of loops and switches and wiggles a lot due to sharp turns.

The switch block is used to represent the if/else logic of the algorithm. This is where the decision to do one action or the other action is done. In the case of the line follower, this is where the robot will know if it will turn left or right.
The loop block is used to tell the robot how many times the action will be performed. For the line follower, the switch block is inside the loop block and the robot will perform the color reading according to the number of times indicated in the loop block.

The pseudocode for this kind of follower is as follows:
- Take a new light sensor reading.
- Compare the reading to the set threshold value. To set the robot just at the edge of the line, the threshold value should be set to 50.
- If the condition is true, turn the motor to the right.
- If the condition is false, turn the motor to the left.

This is a sample program for a switch line follower. The sensor will check if it senses black or white. If it reads white (> 50), the robot will turn right sharply. If it reads black (< 50), the robot will turn left sharply. This action is placed inside a loop and the programmer can dictate how long the robot should perform this action.
Proportional Line Follower
The other line follower to be discussed is the Proportional Line Follower. It is more sophisticated than the switch line follower because it uses Math Blocks and Data Wires. With the use of these blocks, the robot can take readings and do corrections based on the readings.
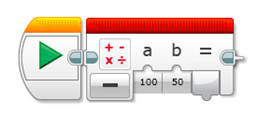
The Math block is used to perform mathematical operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication and division.
The data wire is used to take an output data from one block and used it as input data in another block.

The pseudocode for the Proportional Line Follower can look like this:
- Reset the Rotation sensor (Only required for line following for a total distance)
- Take a new light sensor reading.
- Compute the error. Distance from line = Light sensor reading – Target reading
- Scale the error to determine a correction amount. Adjust the scaling factor to make the robot follow the line smoothly.
- Use the correction value (from Step 4) to adjust the robot’s turn towards the line.
This is a sample program:

- Step 1 is to reset the rotation sensor.
- Step 2 is when the color sensor will take a light reading and input it into the Math block as variable a.
- Step 3 is when the Math block will compute the error which is a – b. Then the output will be inputted to the next Math block which is Step 4.
- In Step 4, the Math block will multiply the error by a scaling factor or a Constant of Proportionality. This scaling factor is based on the robot design and can be usually determined thru trial and error. The correction will then be inputted to the move steering block to adjust the robot’s turn towards the line.
- Steps 2 – 5 are inside the Loop block and can be performed according to what the programmer needs.
These two Line Followers are the most commonly used. Aside from these two, what other kind of line follower do you know or have you created by yourself?
Sources:
https://ev3lessons.com/en/ProgrammingLessons/advanced/LineFollower.pdf
https://ev3lessons.com/en/ProgrammingLessons/advanced/ProportionalLineFollower.pdf






Responses